Reading Notes on Instruction Finetuning
Instruction Tuning and FLAN
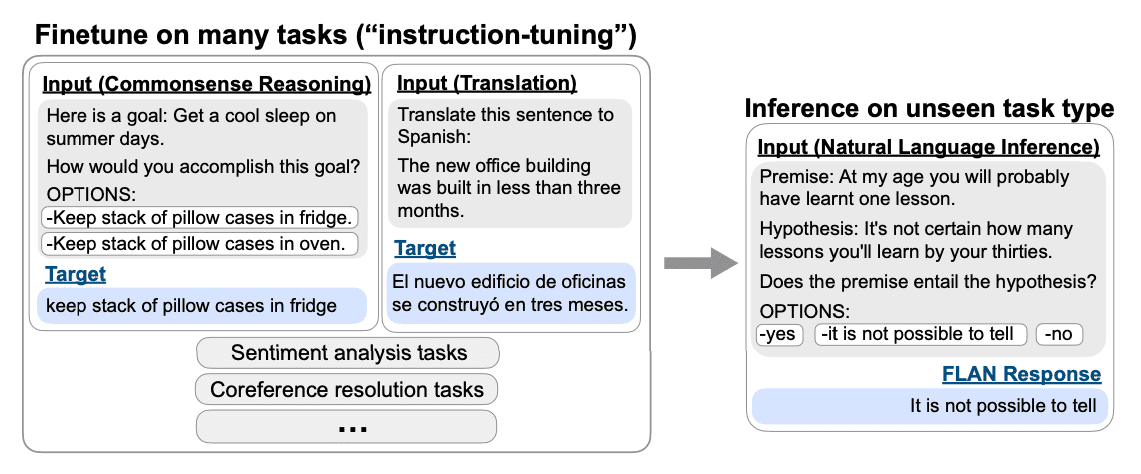
- Finetuned Language Models Are Zero-Shot Learners was published at ICLR 2022 and introduced Instruction Finetuning
- Background: LMs have shown good performances as few-shot learning but not as much at zero-shot learning. Without few-shot examples, it’s hard for the model to perform well on prompts that are not similar to the pretraining data
- In order to improve the zero-shot performance, Wei et al. turned different NLP tasks into natural language instructions, e.g. Is the sentiment positive or negative, translate “how are you” into Chinese. All tasks are formatted into the Causal LM task.
- Running Instruction Tuning on a large LM with 60+ NLP datasets expressed via instructions resulted in FLAN, which substantially improves the zero-shot performance
- Ablation observation 1: increasing the number of task types in instruction tuning improves performance on unseen tasks
- Ablation observation 2: the benefits of instruction tuning emerge only with sufficient model scale, as instruction tuning hurts the performance for models that are 8B or smaller. One potential explanation is that for small-scale models, learning the ∼40 tasks used during instruction tuning fills the entire model capacity, causing these models to perform worse on new tasks
- Instruction Tuning vs. finetuning vs. prompt tuning
- Finetuning: Model learns one specific task. Requires many task-specific examples. Runs on seen task and unseen data at inference time.
- Prompt Tuning: Model learns one specific task. Prompting improves few-shot performance by reducing the number of required task-speicic examples. Runs on seen task and unseen data at inference time.
- Instruction Finetuning: model learns to perform many tasks via natural language instructions. Runs on unseen task and unseen data at inference time
Advancing Instruction-Finetuned Models
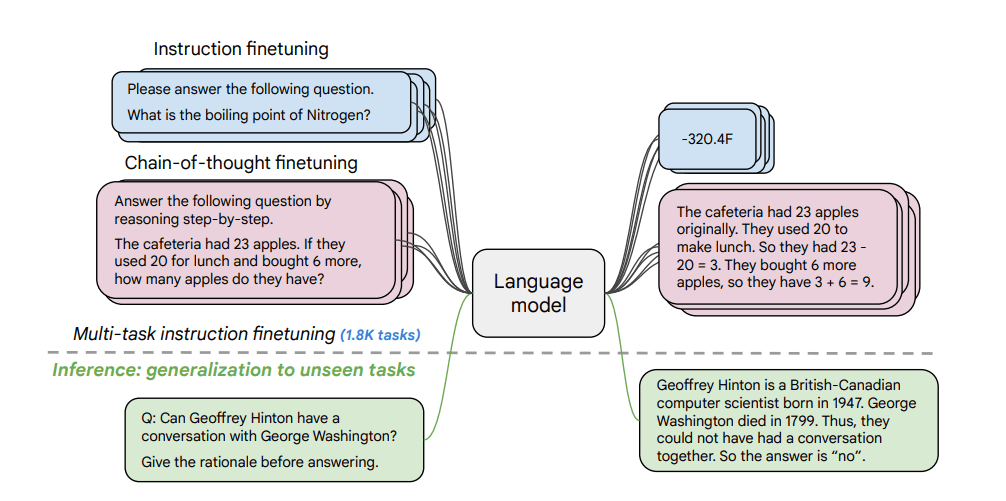
- Google reseachers Chung et al. published Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models in late 2022, which showed that instruction finetuning can improve performance across a range of model architectures, model sizes, prompting setups, and evaluation tasks
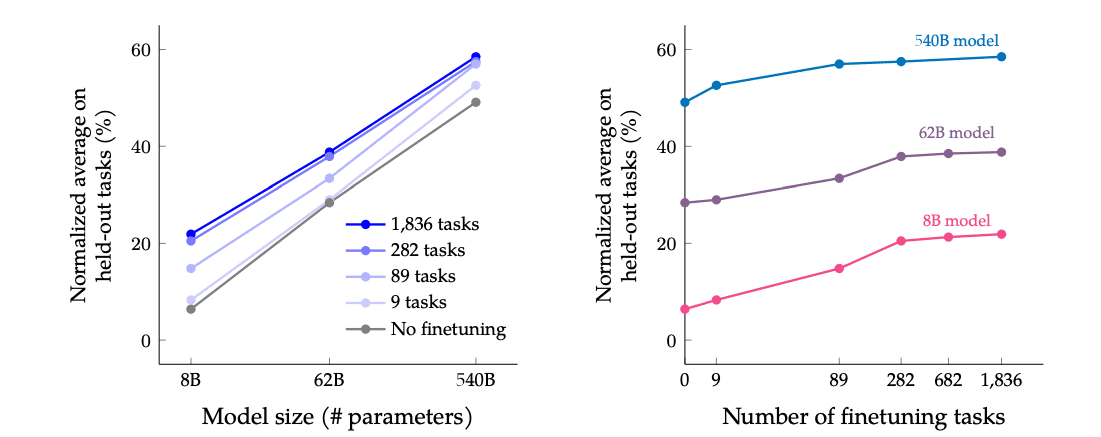
- Key contribution 1: scaled model sizes 137B -> 540B and number of tasks 62 -> 1836
- Across all three model sizes (8B, 62B, 540B) of PaLM, instruction finetuning improves performance by a large margin
- Increasing the number of finetuning tasks improves performance but the gain diminishes after 282 tasks
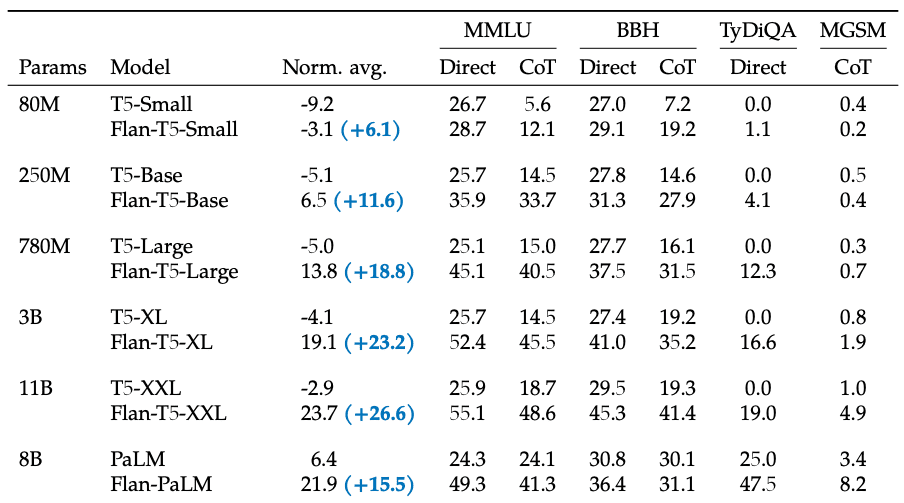
- Key contribution 2: Added encoder-decoder architecture (T5) and open-sourced Flan-T5 checkpoints, which achieve strong few-shot performance even compared with much larger models
- Flan-T5-Small with 80M params has similar zero-shot performance as T5-XXL 11B
- Flan-T5-Base with 250M params has similar zero-shot performance as PaLM 8B
- Key contribution 3: introduced chain-of-thought data, which improves multi-step reasoning ability